Abstract
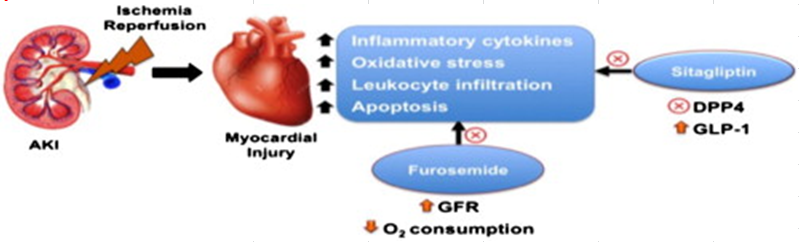
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is associated with high mortality resulting from extra-renal organ damage, particularly the heart. The present study aimed to investigate the protective effect of sitagliptin, a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP4) inhibitor, against renal and remote cardiac damage induced by ischemia/reperfusion (IR), a leading cause of AKI. In this attempt, we compared the effects of sitagliptin to furosemide, a loop diuretic. Furosemide is commonly used clinically in AKI however, there is a lack of evidence regarding its beneficial effects in AKI. In addition, the combined administration of both drugs was also investigated. Ischemia was induced in anesthetized male Wistar rats by occluding both renal pedicles for 30 min followed by reperfusion for 24 h. Sitagliptin (5 mg kg−1), furosemide (245 mg kg−1) or their combination were administered orally at 5 h post-IR and 2 h before euthanasia. Administration of sitagliptin or furosemide ameliorated renal and cardiac deterioration induced by renal IR. This was manifested as significant reduction of serum creatinine, urea, cystatin c, creatine kinase-MB, cardiac troponin-I and lactate dehydrogenase (P < 0.05). Drug treatment significantly inhibited IR-induced elevation of TNF-α, NF-κB and caspase-3 (P < 0.05) in kidney and heart tissue. In addition, they significantly suppressed malondialdehyde, NO and iNOS content, whereas they increased glutathione and antioxidative enzymes activity (P < 0.05) in both tissues. Interestingly, a superior protection was observed with the combination compared to the individual drugs. We assume that this combination represents a promising regimen for managing AKI, particularly with the poor clinical outcome obtained with furosemide alone.